6. Energy and Emission Trends
This part throws light on the current trend in the evolution of energy sector through technologies and innovation taken towards a cleaner and carbon free world.
Since the formulation of the SDGs in 2015, the world has been trying to cut down its emissions and shift towards cleaner energy alternatives. The three most important emerging energy and emission trends are decentralization, decarbonization and digitalization.
Decentralization[20]
The traditional energy markets are based on the centralized distribution system where the power generated is stored at a distribution center, which diverts it to residentials and industrial/ commercial consumers.
The major demerits of this system:
- Large amounts of generated energy might be lost during transmission from the distribution center
- The energy supply may also be disrupted frequently as the supply is inter-connected.
With the rise of renewables, we are seeing drastic changes in the energy production, distribution and selling. Countries and businesses are opting for testing innovative new approaches apart from the traditional centralized energy networks. The decentralized energy system helps in overcoming these problems. A decentralized energy system is the one where the energy production facility is present closer to the site of energy consumption. A decentralized system includes many distributed small energy generation systems instead of a few larger ones and storage is also done on or off grid based on the energy supply and demand.
Its effects are most noticeable in countries where behind-the-meter (BTM) energy generation, wherein a business or household produces its own energy.

The following table gives an insight into what decentralized energy systems at an individual and commercial level mean.
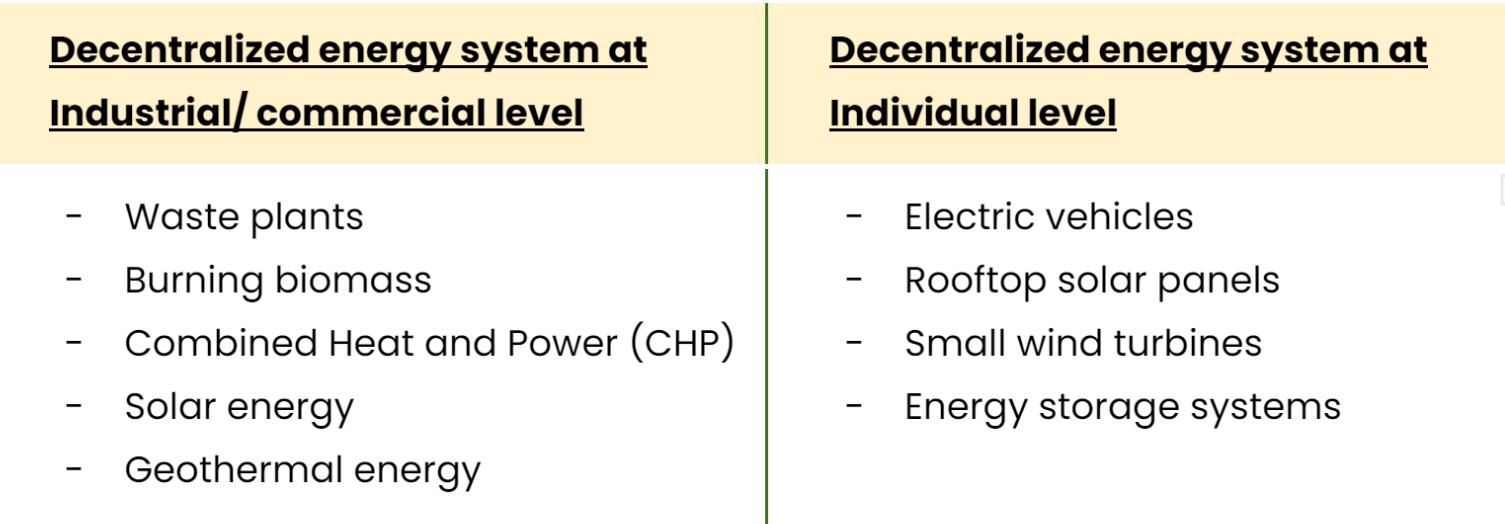
Decentralization of energy helps to minimize the energy loss during transmission, reduce the expenses on transportation of the energy, ensures the uninterrupted supply of energy, increases the dependency on renewable energy sources and improves the energy efficiency.
Decarbonisation:
The present fossil- fuel driven world is moving inevitably towards climate change. The major reason for this fast transition is carbon emissions. Thus, it has become a necessity to curb carbon emissions. Decarbonization refers to transition towards a clean and carbon-free world, largely by reducing or removing the amount of CO2. It is a critical pillar of the larger journey towards Net Zero Emissions.
Example:
1. Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage (CCUS) Technologies- Under this approach, the carbon emissions are captured from large sources like power generation plants. The stored carbon is either used on-site or transported to various places for a wide range of applications.
Bharat Heavy Electronics limited (BHEL) has indigenously design, developed and installed a carbon capture plant[21].
2. Green Hydrogen- Hydrogen produced from the electrolysis of water powered by renewable sources of energy is termed as ‘green hydrogen’, because it is clean and sustainable. The uses of the GH2 (Green Hydrogen) are-
- It is versatile- can be used as fuel in industries or be converted to electricity in fuel cells.
- Has no geographical restrictions and is easy to transport. Thus, ensures energy security.
- Its derivatives like green ammonia and green methanol are long- term energy carriers. Therefore, they can be used to store surplus renewable energy.
India’s first Green Hydrogen Fuel Cell Bus has been developed by Indian Oil Corporation (IOC) and 15 buses were run in the NCR for trial[21].
3. Electrification- Currently, the world is depending on fossil fuel based automotives for transportation and commuting. Vehicular emissions are also one of the major contributors of GHGs. Thus, switching to electric vehicles also helps to reduce vehicular emissions.

Did you know?
By the end of 2021, over one third of the world’s 2,000 largest publicly traded firms had already set net-zero targets.[22]
Digitalization [23]
Digitalization is an emerging trend revamping the energy landscape and enabling continuous energy efficiency improvements and smooth transitioning towards cleaner energies. Digital technologies and digitalization help reduce carbon emissions by:
- Improving energy efficiency
- Optimizing energy management
- Coordinating supply and demand in an increasingly decentralized electricity distribution network
- Improving operational process efficiency across industry sectors.
Artificial Intelligence, Blockchain technology and the Internet of Energy are three major tools that play a crucial role in digitalization of the energy sector.

1. Artificial Intelligence (AI)- Helps to forecast demand, manage the distribution of resources, ensure the availability of power when needed with minimal waste (feature useful in case of renewable energy). The AI logarithms are also helpful in decentralization of the energy systems and prediction of the individual/ industrial carbon footprints, aiding people in making educated decisions.
2. Blockchain Technologies- This technology helps to ensure security and transparency by recording all trades, payments or negotiations in the energy sector.
3. Internet of Energy (IoE)- IoE processes information from the source (point of power generation or consumption) with the help of sensors, scanners and through remote data centers. This will aid the utility companies in data-driven decision-making and predictive maintenance to improve energy efficiency and consumer satisfaction.
Moreover, digital technologies will be essential for the management of carbon capture and storage and the conversion of fossil fuel-based transportation towards electrified and automated transportation. It will help in monitoring, exception- based surveillance, prediction analytics , AI - assisted decision- making digital technologies.
Additional Information
Enroll in courses
Energy, Environment and Everyday Life|Coursera