4: Emission Patterns
Emissions have been further categorised into 3 types to understand its sources and severity and thereby include stratergies to the path of decarbonisation.
Now that we know, emissions are one of the major causes of air pollution, it is time to understand the emission patterns. The term ‘emissions’ is used to describe the gases and particles released into the atmosphere by various sources. These emissions are majorly greenhouse gases (GHGs) that contribute to global warming. The release of these GHG emissions depends on its sources and other related factors like the country's economy, industrial activity, technology advancements, daily traffic, and others.
Emissions are classified under international standards as the emissions from one country can affect other countries. Understanding the emission trends will help to be informed about the emission source, level of its impact and also helps to plan mitigation measures to reduce the impact. Depending upon the business activities of industries / companies the emissions are classified into Scope 1, Scope 2, Scope 3 and Scope 4 emissions.

Scope 1 Emissions
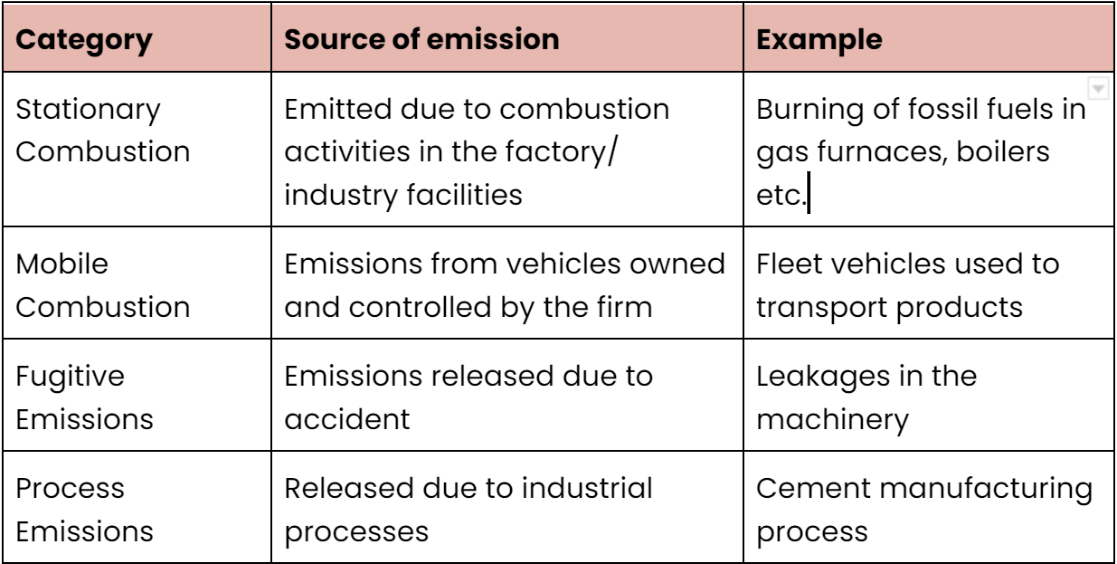
These are direct GHGs that come from a source where the fuel is burnt on sites/ facilities owned and controlled by the company/ organisation. They are further categorised into 4 categories based on the cause of the emissions-
Scope 2 Emissions
These emissions are indirect emissions of GHGs associated with the company’s/ organisation’s electricity or energy consumption. The most common example of scope 2 emission include purchase of electricity, steam, heat, or cooling. Though, the emissions occur at the source of energy/ electricity generation, they are accounted as the firm's emission because of its usage.
Scope 3 Emissions
These are indirect emissions from all the activities (upstream and downstream) of the company. It includes all the emissions that are not included in the scope 1 and scope 2 categories. The example of scope 3 emission are production of goods, transportation of purchased fuel, buying products from its suppliers and using those produced goods.
Scope 4 Emissions
Also known as ‘Avoided Emissions’, scope 4 has been recently added to the list of emission trends by ‘World Resource Institute’ , a non- profit organisation. It can be described as reduction in emission occurring outside the lifecycle of the product or its value chain, but as a result of the use of the product.