3. Material Circularity
How resources and materials can be best utilized.
Material Circularity can be explained as the characteristic to increase the usage of resources and material, by processes such as recycling, repair, reuse and redesign. It helps to lessen the demand for new raw materials and the associated negative environmental effects like greenhouse gas emissions and deforestation.
The following are the ways to increase material circularity:
- Design for recyclability: Designing products with recyclable materials and minimal waste, so that they are conveniently disassembled and their components can be recovered at the end of their life.
For Example, the tyres are made of rubber, metal and fibre. Recycling or dismantling of the old, worn out tyres can help recover the rubber and metal, which can be used in the manufacture of new tyres or other such products. - Increase Recycling rates: Increasing the effectiveness and efficiency of recycling systems to enable the recovery and reuse of a greater volume of materials.
For instance, if the recycling efficiency and rates of plastic is high, then it is less likely that the plastic containers, products and other waste will end up in the landfills. - Repair and reuse: Promoting reuse and repair of products rather than replacing with new ones. This may lessen the need for new materials and increase the usable life of products.
Example; Instead of discarding the phones that are not working and we can use them after repair, give it to the recycler or refurbish it. - Product as a service: Businesses can provide a service that enables customers to enjoy a product's benefits without purchasing it as an alternative to selling the product.
This can be best explained through the classic example of a library, a place of knowledge in the form of books. In any library, a person can access any book without actually buying it.
Overall, material circularity is a crucial component of the circular economy as it reduces the need for new raw materials and ensures reduced environmental impacts while simultaneously generating economic opportunities through material reuse and recycling.
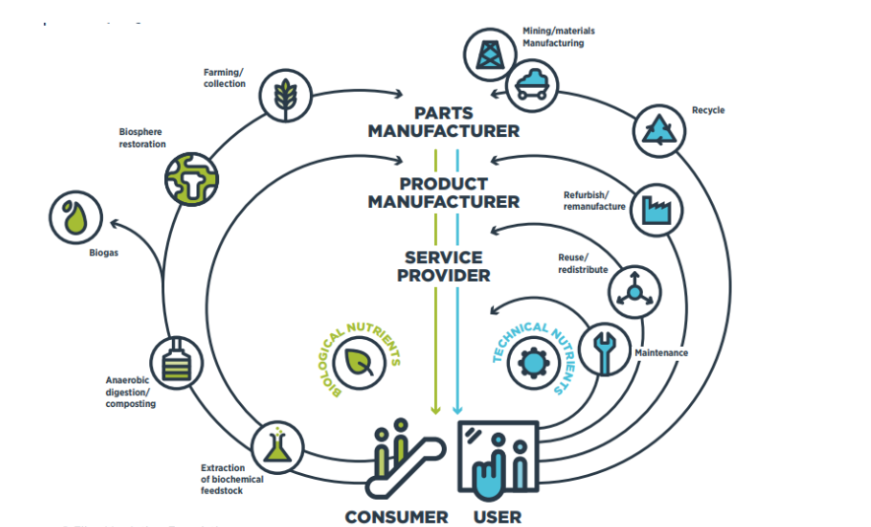
The Butterfly Diagram
The circular economy model can be visually represented by a butterfly diagram which shows how resources and materials move through a closed-loop system. The illustration is known as a "butterfly" because its two wings, which stand in for the technical and biological flows of the circular economy, mimic the shape of a butterfly.[2]
The butterfly graphic demonstrates how these two flows are intertwined, with materials and resources going back and forth between the biological and technology systems and being continually utilized.
* Technical Flow:
It describes how resources and materials are moved throughout the industrial system. This includes the extraction and processing of raw materials, the production of goods, and the recycling and reuse of materials.
The loops in this flow represent different processes that help to keep the product in the loop. The processes in the inner loops (Maintenance, Reuse/Redistribute, Refurbish/Remanufacture) can help extract more value to the product compared to the outer loop process (Recycle). This is because the product will be in a good condition when in the inner loop and recycling is the last resort when the product can’t be used any further.
Let us understand this with an example of a mobile phone. We can share it, repair and upgrade it, and resell the mobile till it is working. Once it stops working, we will give it to the recycler.
* Biological Flow:
It involves the movement of resources and materials through the natural system. It includes the development and harvesting of crops, the preparation of food and other biological products, as well as the composting and recycling of organic waste.
This flow focuses on nature restoration by using organic and eco- friendly methods. It promotes organic farming practices and after use by the consumer, it is further processed with the help of microbes to extract biogas. The rest of the solid matter returns to the soil.
Note : The butterfly diagram is a helpful tool for understanding how the circular economy model works to reduce waste and lengthen the lives of commodities. It can be used to find chances to increase material circularity and lessen the effects of economic activities on the environment.